How To Find Skew Of Data Set
We consider a random variablex and a information fixS ={x i , x ii , …, tendue north } of size n which contains possible values of10. The data set can represent either the population beingness studied or a sample drawn from the population.
Looking at Due south as representing a distribution, the skewness of S is a measure of symmetry whilekurtosis is a measure of peakedness of the data in S.
Symmetry and Skewness
Definition 1: We employ skewness as a measure of symmetry. If the skewness of South is zero and then the distribution represented by S is perfectly symmetric. If the skewness is negative, so the distribution is skewed to the left, while if the skew is positive then the distribution is skewed to the right (see Figure i below for an example).
Excel calculates the skewness of a sampleS every bit follows:
![]()
where x̄ is the mean and s is the standard departure of Southward. To avert division by zero, this formula requires that northward > two.
Ascertainment: When a distribution is symmetric, the mean = median, when the distribution is positively skewed the mean > median and when the distribution is negatively skewed the mean < median.
Excel Office: Excel provides the SKEW function as a mode to calculate the skewness of S, i.east. if R is a range in Excel containing the data elements in South then SKEW(R) = the skewness of S.
Excel 2022 Office: In that location is as well a population version of the skewness given by the formula
![]()
This version has been implemented in Excel 2022 using the part, SKEW.P.
Information technology turns out that for range R consisting of the data in S = {x 1, …,10due north }, SKEW.P(R) = SKEW(R)*(n–2)/SQRT(n(n–one)) where north = COUNT(R).
Existent Statistics Role: Alternatively, you tin can calculate the population skewness using theSKEWP(R) role, which is contained in the Real Statistics Resource Pack.
Instance 1: SupposeS = {2, 5, -1, 3, 4, 5, 0, two}. The skewness ofSouth = -0.43, i.e. SKEW(R) = -0.43 where R is a range in an Excel worksheet containing the data in S. Since this value is negative, the bend representing the distribution is skewed to the left (i.e. the fatter office of the bend is on the correct). Besides SKEW.P(R) = -0.34. See Figure 1.
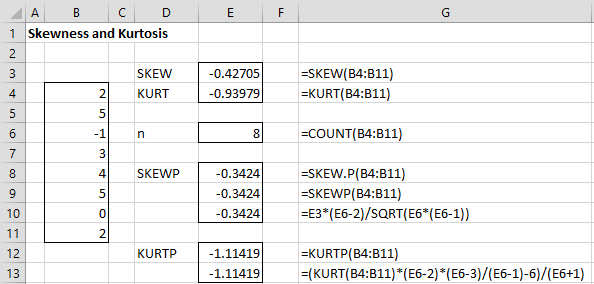
Figure 1 – Examples of skewness and kurtosis
Observation: SKEW(R) and SKEW.P(R) ignore whatsoever empty cells or cells with not-numeric values.
Kurtosis
Definition 2: Kurtosis provides a measurement nigh the extremities (i.e. tails) of the distribution of information, and therefore provides an indication of the presence of outliers.
Excel calculates the kurtosis of a sampleSouth as follows:
![]()
where x̄ is the mean and southward is the standard deviation of S. To avert division by zero, this formula requires thatn > 3.
Observation: It is commonly thought that kurtosis provides a measure of peakedness (or flatness), but this is not true. Kurtosis pertains to the extremities and not to the center of a distribution.
Excel Function: Excel provides theKURT function every bit a way to calculate the kurtosis ofDue south, i.e. if R is a range in Excel containing the data elements in S and then KURT(R) = the kurtosis of S.
Observation: The population kurtosis is calculated via the formula
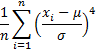
which can exist calculated in Excel via the formula
=(KURT(R)*(northward-2)*(n-3)/(north-1)-6)/(northward+1)
Real Statistics Function: Excel does non provide a population kurtosis part, merely you can utilise the following Real Statistics function for this purpose:
KURTP(R, excess) = kurtosis of the distribution for the population in range R1. If excess= Truthful (default) then three is subtracted from the result (the usual arroyo so that a normal distribution has kurtosis of zero).
Example 2: SupposeS = {2, v, -1, 3, 4, 5, 0, two}. The kurtosis of S = -0.94, i.e. KURT(R) = -0.94 where R is a range in an Excel worksheet containing the data in S. The population kurtosis is -1.114. See Effigy 1.
Ascertainment: KURT(R) ignores any empty cells or cells with non-numeric values.
Graphical Illustration
We at present look at an example of these concepts using the chi-square distribution.
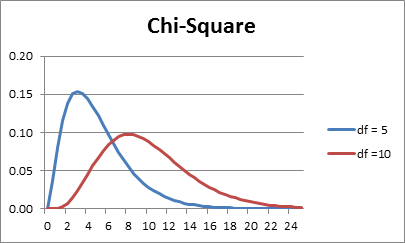
Figure 2 – Instance of skewness and kurtosis
Figure 2 contains the graphs of two chi-foursquare distributions (with different degrees of freedom df). We study the chi-square distribution elsewhere, but for now notation the following values for the kurtosis and skewness:
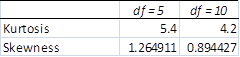
Figure three – Comparison of skewness and kurtosis
Both curves are asymmetric and skewed to the right (i.east. the fat role of the bend is on the left). This is consistent with the fact that the skewness for both is positive. But the blueish bend is more skewed to the correct, which is consistent with the fact that the skewness of the blue curve is larger.
How To Find Skew Of Data Set,
Source: https://www.real-statistics.com/descriptive-statistics/symmetry-skewness-kurtosis/
Posted by: maronepaide1972.blogspot.com


0 Response to "How To Find Skew Of Data Set"
Post a Comment